The Cardiac Muscle Is Capable of Which of the Following
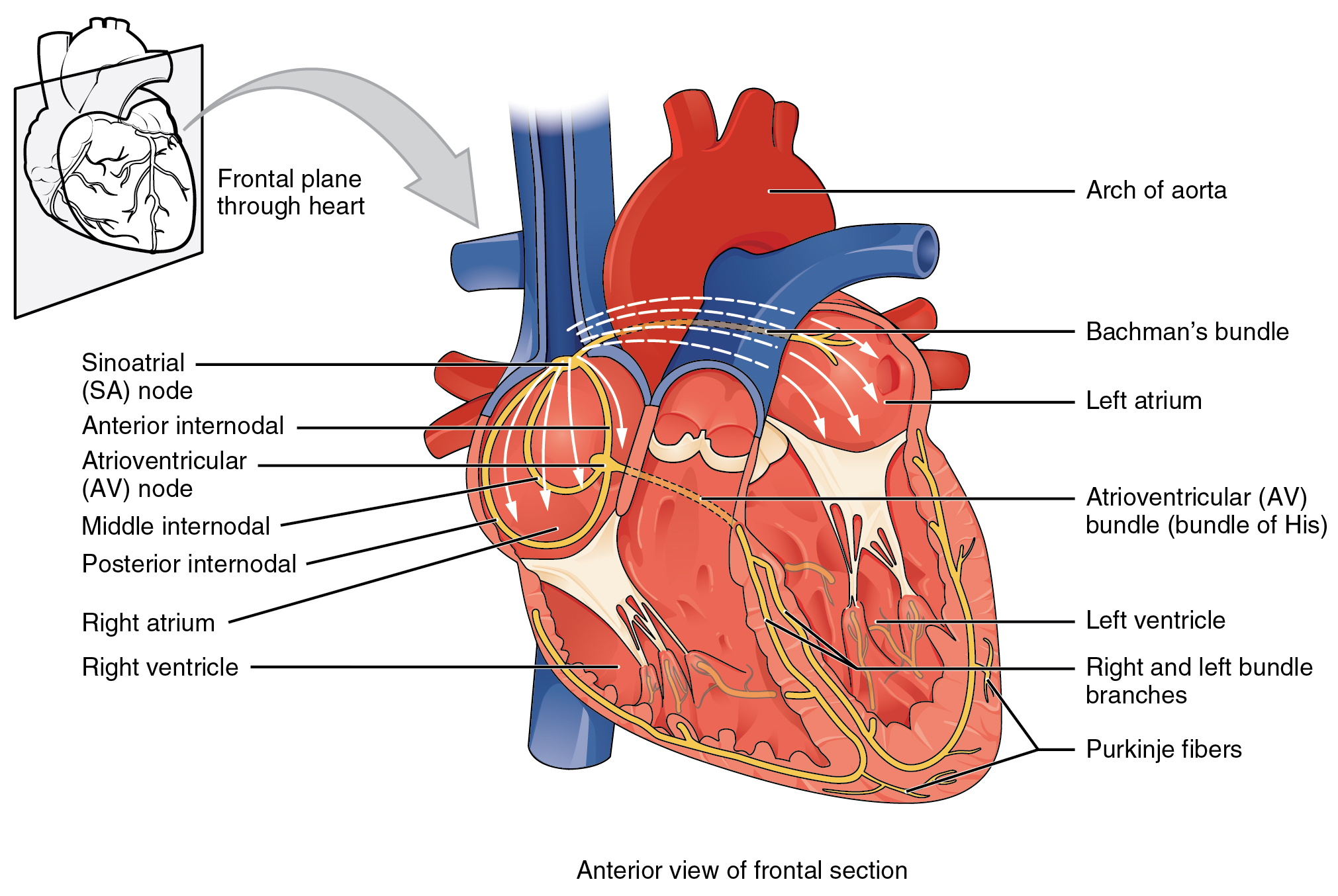
Impulse arrives at the AV node where there is a momentary delay because action potentials are transmitted more slowly in these cells than in other cells of the conduction system. Also known as myocardiocytes cardiomyocytes are cells that make up the heart musclecardiac muscle.
Cardiac Muscle Tissue Anatomy Physiology
Myocardial dysfunction and vascular instability are common following resuscitation from cardiac arrest.
. Another important ionic current capable of depolarizing the cell is the sodium-calcium exchanger current I NCx. Figure 1921 Cardiac Muscle. 9 Athletes use concentric contractions to counter a load.
Only cardiac muscle has gap junctions. When a muscle is being stimulated but is not able to respond because of oxygen deficit rhe condition is called is a contraction in which the muscle does not G. Cardiac muscle is only found in the heart and although it is striated like skeletal muscle it functions involuntarily.
Pacemaker cells are primarily located in the sinoatrial SA node and atrioventricular AV node. Cardiac and most smooth muscles are autorhythmic-they are capable of contracting spontaneously without nervous or hormonal stimulation. A Cardiac muscle cells have myofibrils composed of myofilaments arranged in sarcomeres T tubules to transmit the impulse from the sarcolemma to the interior of the cell numerous mitochondria for energy and intercalated discs that are found at the junction of different cardiac muscle cells.
420 The postarrest effects on the cardiovascular system may evolve over time with an initial hyperdynamic state replaced by worsening cardiac. Which of the following is unique to cardiac muscle cells. The heart contracts or beatscardiac striated and involuntary.
Concentric contraction involves shortening of the muscle with requisite movement of the origin or insertion and limb translation. Only cardiac muscle has a high concentration of mitochondria. 414 419 Systemic and pulmonary vascular resistances are often increased initially except in some cases of septic shock.
Impulse leaves the AV node and travels. An action potential is initiated in the SA node and travels by way of conduction fibers to the AV nodeAction potential spreads throughout the cells of the atria. An shorten but tension in rhe muscle keeps increasing.
Late phase 3 EAD-induced extrasystoles have been shown to initiate AF in canine atria particularly following spontaneous termination of the arrhythmia IRAF immediate reinduction of AF. When a weak but smooth muscle contraction is desired are stimulated ar a rapid rate. In human beings as well as many other animals cardiomyocytes are the first.
They are used to accelerate the distal segment of the limb and attached equipment such as a racquet or ball. Only cardiac muscle contains a sarcoplasmic reticulum. A cardiac pacemaker or artificial pacemaker so as not to be confused with the natural pacemaker of the heart is a medical device that generates electrical impulses delivered by electrodes to cause the heart muscle chambers the upper or atria andor the lower or ventricles to contract and therefore pump bloodBy doing so this device replaces andor regulates the.
As the chief cell type of the heart cardiac cells are primarily involved in the contractile function of the heart that enables the pumping of blood around the body. Cardiac muscle cells are also called cardiac myocytes cardiomyocytes or myocardiocytes. B A photomicrograph of cardiac muscle cells.
Only cardiac muscle is capable of autorhythmicity d. The pacemaker cells are specialized cardiac myocytes that are capable of generating spontaneous action potentials and are responsible for cardiac conduction. Unlike a graded potential an action potential is capable of traveling long distances.
48 The appearance of late phase 3 EAD immediately. The terms in the key refer to. Dugan in Clinical Sports Medicine 2007 Concentric.
With skill training the. The following four steps describe the initiation of an impulse to the resetting of a neuron to prepare for a second stimulation.

Papillary Muscle Anatomy Britannica

Cardiac Muscle And Electrical Activity Anatomy And Physiology
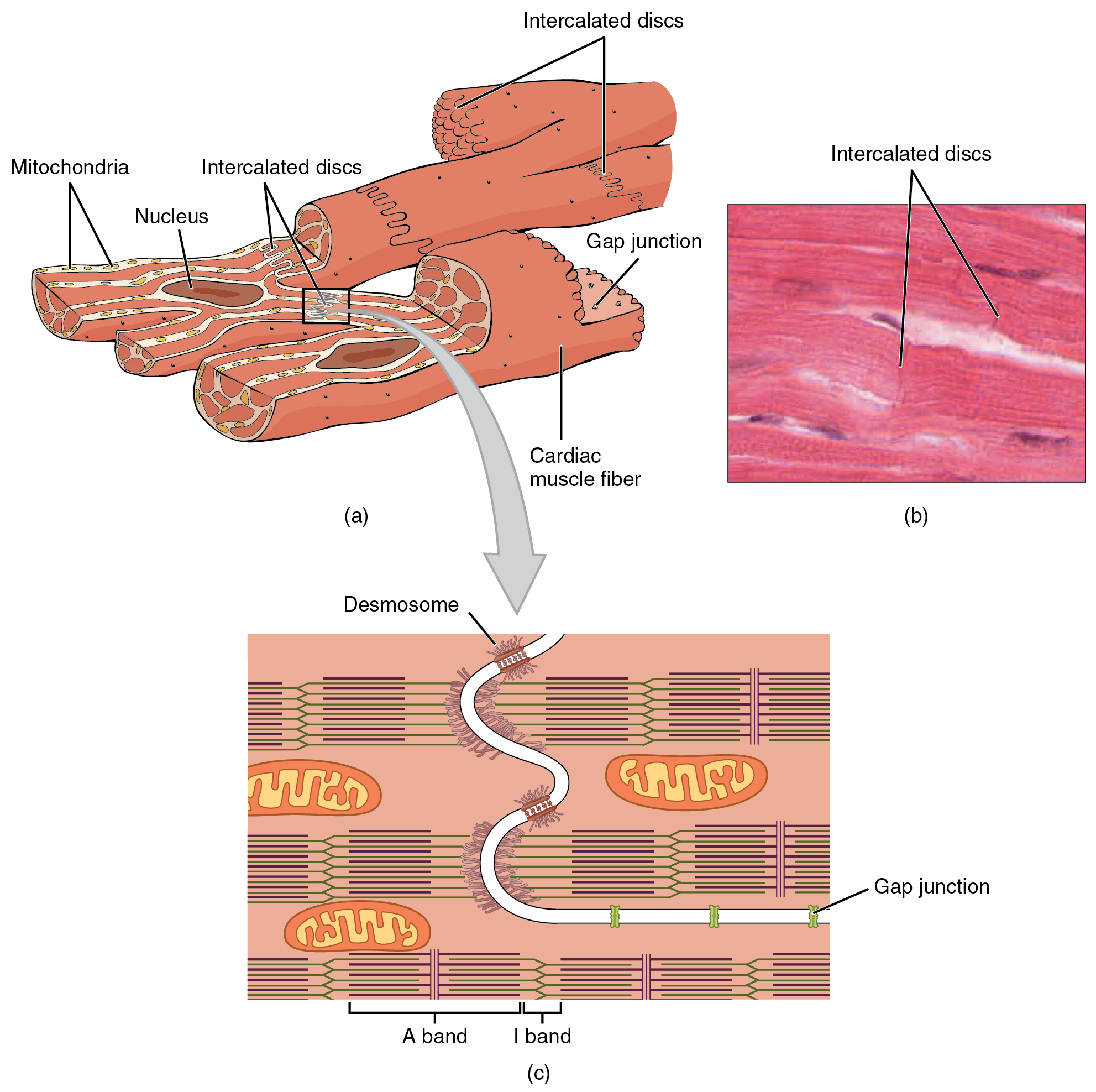
Cardiac Muscle And Electrical Activity Anatomy And Physiology

Human Medical Physiology Q A Absolute Vs Refractory Period Of Cardiac Muscle Cells Physiology Refractory Period Studying Medicine

Comments
Post a Comment